
Towards the integrative theory of Alzheimer's disease: linking molecular mechanisms of neurotoxicity, beta-amyloid biomarkers, and the diagnosis

Membrane channel hypothesis of lysosomal permeabilization by beta-amyloid

Designed Cell-Penetrating Peptide Inhibitors of Amyloid-beta Aggregation and Cytotoxicity - ScienceDirect

Monomeric and Aggregated Tau Enter Neurons via Different Mechanisms (A)

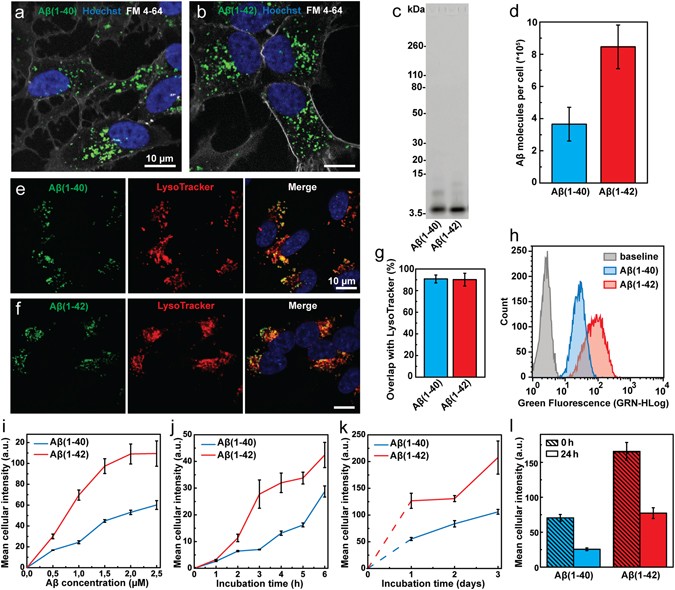
Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin- independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ (1–40)

In vivo synaptic activity-independent co-uptakes of amyloid β1–42 and Zn2+ into dentate granule cells in the normal brain
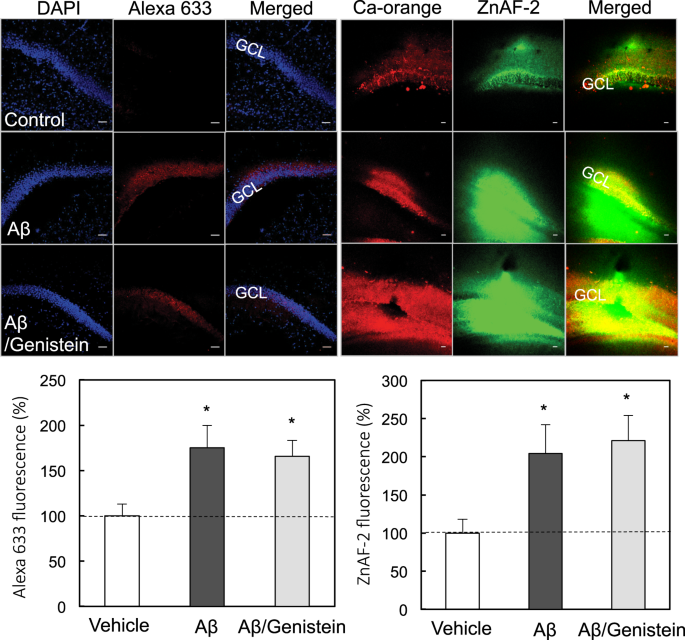
In vivo synaptic activity-independent co-uptakes of amyloid β1–42 and Zn2+ into dentate granule cells in the normal brain

Amyloids facilitate DNA transfection in vivo - ScienceDirect

Endocytosis Is a Key Mode of Interaction between Extracellular β-Amyloid and the Cell Membrane - ScienceDirect