By A Mystery Man Writer
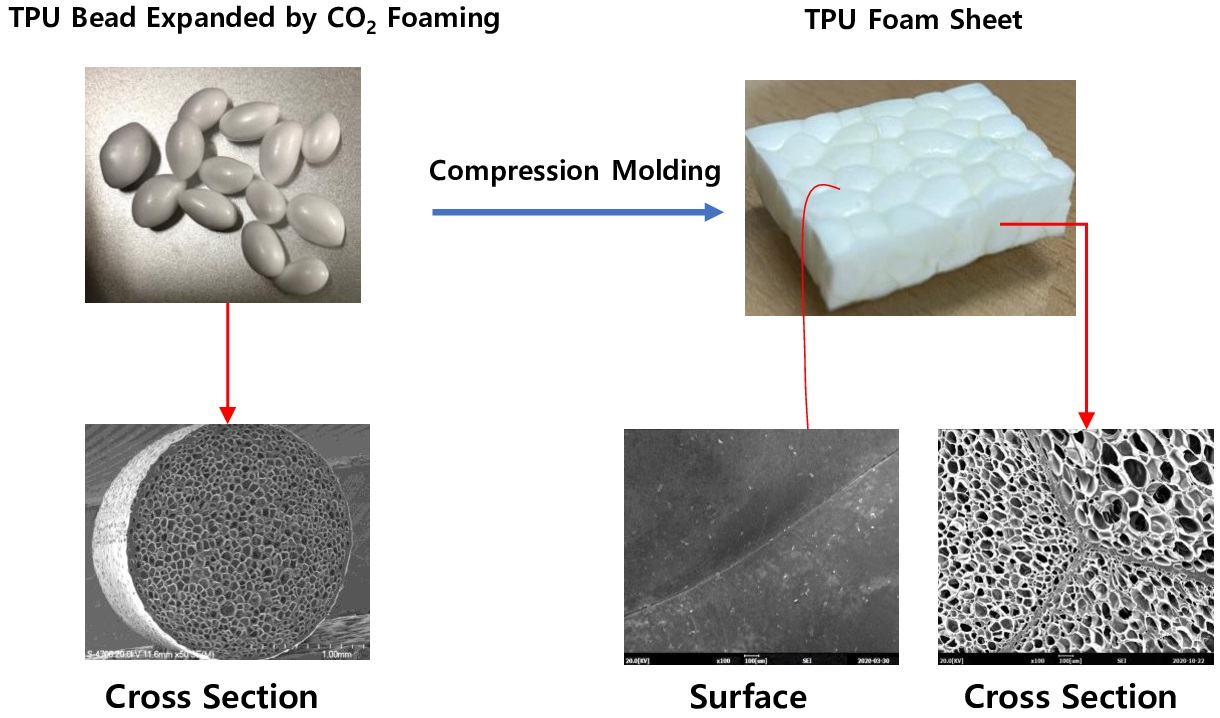
Expanded thermoplastic polyurethane (ETPU) beads were prepared by a supercritical CO2 foaming process and compression molded to manufacture foam sheets. The effect of the cell structure of the foamed beads on the properties of the foam sheets was studied. Higher foaming pressure resulted in a greater number of cells and thus, smaller cell size, while increasing the foaming temperature at a fixed pressure lowered the viscosity to result in fewer cells and a larger cell size, increasing the expansion ratio of the ETPU. Although the processing window in which the cell structure of the ETPU beads can be maintained was very limited compared to that of steam chest molding, compression molding of ETPU beads to produce foam sheets was possible by controlling the compression pressure and temperature to obtain sintering of the bead surfaces. Properties of the foam sheets are influenced by the expansion ratio of the beads and the increase in the expansion ratio increased the foam resilience, decreased the hardness, and increased the tensile strength and elongation at break.

PDF) POLYMER BLENDS HANDBOOK GOPALAKRISHNAN DURAISAMY

Polymerization, Definition, Classes, & Examples

Polymers, Free Full-Text
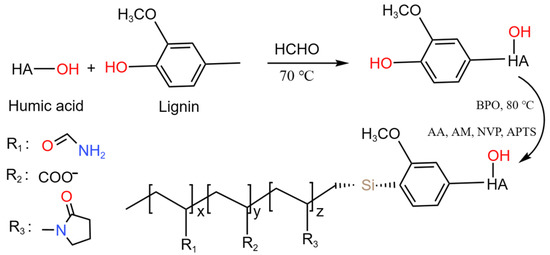
Polymers, Free Full-Text
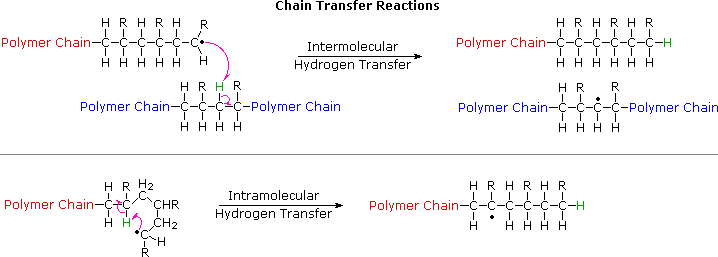
Polymers

Polymer - BI without the BS
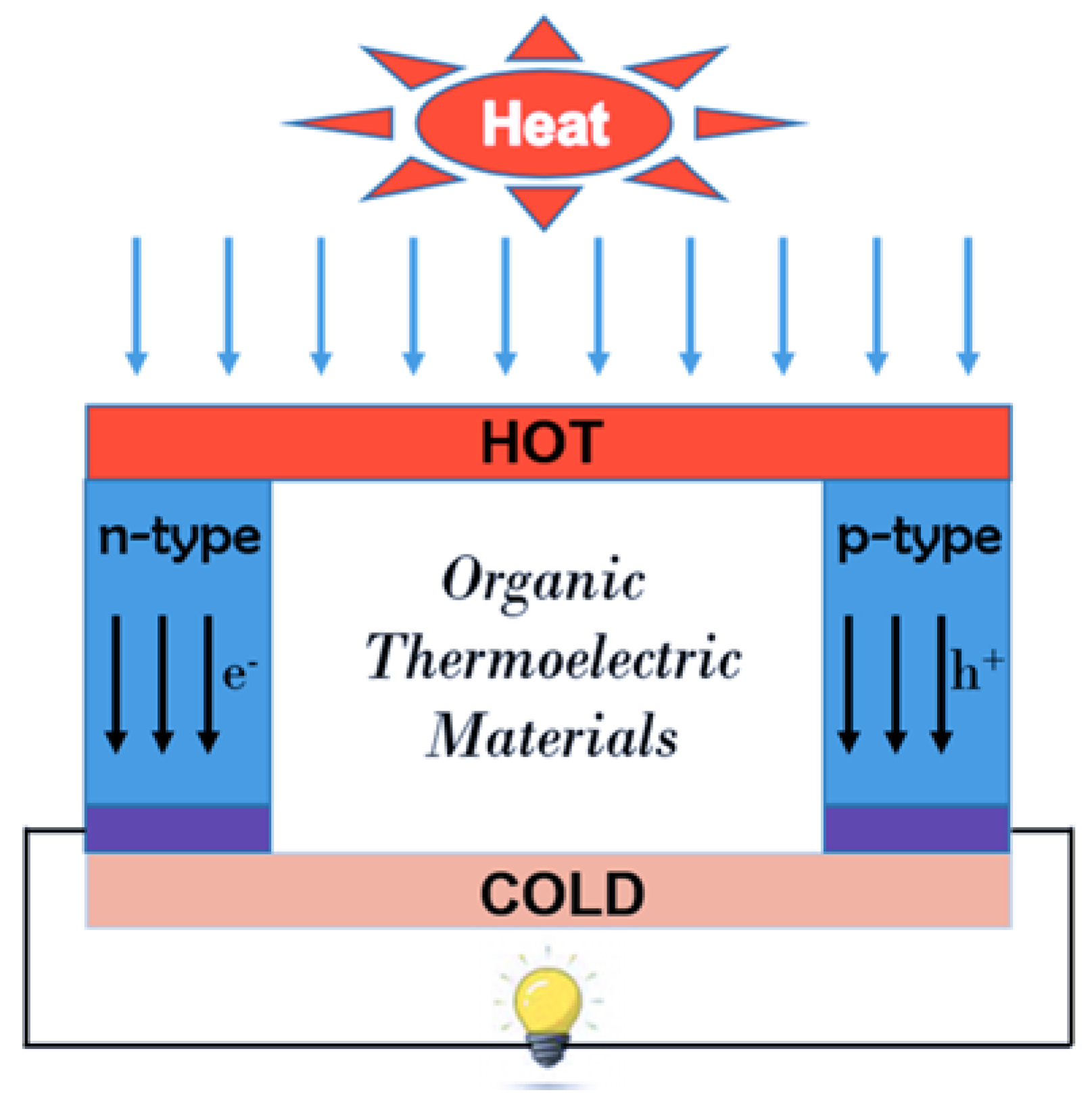
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Polymers, Free Full-Text, nmm2 values

Polymers, Free Full-Text, benny watts x reader

Fundamentals of Polymer Science: An Introductory Text [Second edition] 9780203755211, 0203755219, 9781351446396, 1351446398

Polymers - Classification, Types, Uses, Properties and Polymerization
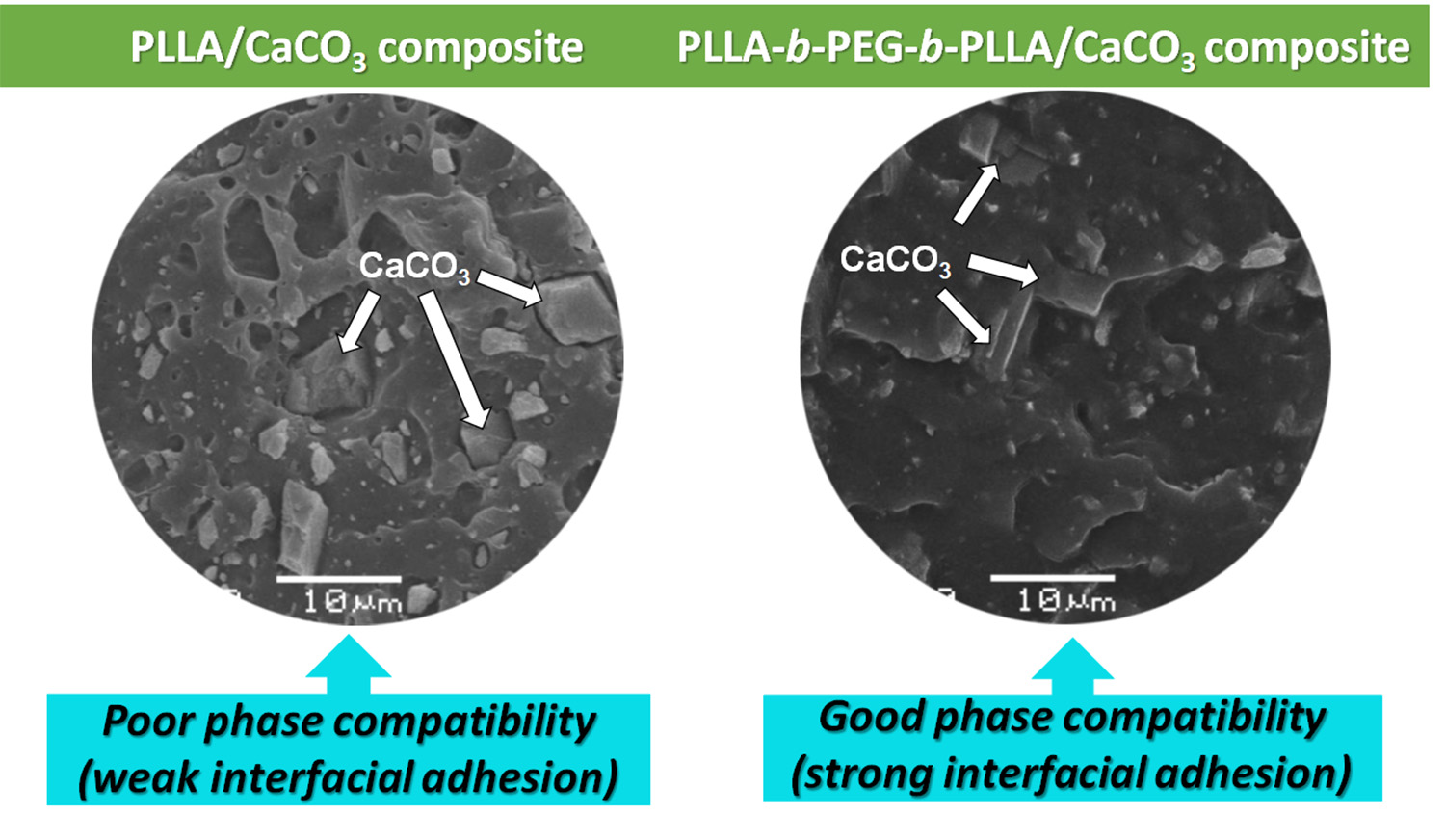

Polymers, Free Full-Text

Polymers, Free Full-Text

High free volume polymers for pervaporation - ScienceDirect